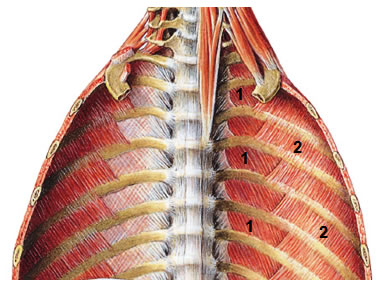
Chest Muscles
The thorax is located in the upper region of the trunk, it is defined anteriorly by the sternum, laterally by the ribs and posteriorly by the vertebral column.
The chest muscles are structured in 2 regions:
- Anterolateral Region
- coastal region
| Anterolateral Region | coastal region |
| Pectoral Major Pectoral Minor serratus anterior subclavian | External Intercostals Internal Intercostals Rib Lifters subcostal transverse thorax |
Anterolateral Region
1. MAJOR CHEST
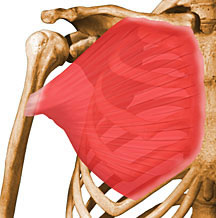 Medial Insertion : Medial 1/2 of the anterior border of the clavicle, anterior surface of the sternum, external surface of the 1st to 6th costal cartilages and aponeurosis of the external oblique of the abdomen
Medial Insertion : Medial 1/2 of the anterior border of the clavicle, anterior surface of the sternum, external surface of the 1st to 6th costal cartilages and aponeurosis of the external oblique of the abdomen
Lateral Insertion : Crest of the greater tubercle
Innervation : Lateral Pectoral Nerve and Medial Pectoral Nerve (C5 – T1)
Action : Adduction, Medial Rotation, Flexion and Horizontal Flexion of the Shoulder
2. MINOR CHEST
I 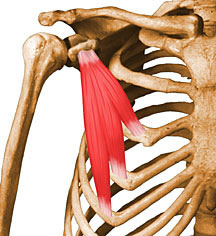 Superior insertion: Coracoid process
Superior insertion: Coracoid process
Inferior Insertion : External surface of 3rd, 4th and 5th ribs
Innervation : Medial Pectoral Nerve (C8 - T1)
Action :
* Fixed in the Chest : Shoulder Depression and Inferior Rotation of the Scapula
* Fixed on the Scapula : Raises the ribs (inspiratory action)
3. SERRATIL ANTERIOR
Posterior Insertion : Medial border of scapula
Bottom Portion :
Posterior Insertion : Inferior angle of scapula
Anterior Insertion : External surface of 5th to 9th ribs
Innervation : Long Thoracic Nerve (C5 - C7)
* Fixed on Scapula : Inspiratory Action
* Fixed in the Ribs : Superior Rotation, Abduction and Depression of the Scapula and Propulsion of the Shoulder

4. SUBCLAVIO
Lateral Insertion : Lower surface of clavicle
Medial Insertion : 1st rib and costal cartilage
Innervation : Subclavian nerve (C5 – C6)
Action : Depression of the Clavicle and Shoulder
coastal region
1. INTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Superior Insertion : Lower edge of the overlying (upper) rib
Lower Insertion : Upper edge of the infrajacent (lower) rib
Innervation : Corresponding intercostal nerves
Action : Depression of the Ribs (Expiratory Action)
2. EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Superior Insertion : Lower edge of the overlying (upper) rib
Lower Insertion : Upper edge of the infrajacent (lower) rib
Innervation : Corresponding intercostal nerves
Action : Raise the Ribs (Inspiratory Action)
The internal and external intercostal muscles cross each other in an “X”. The fibers of the external intercostals run from superior to inferior and from posterior to anterior. The fibers of the internal intercostals run from superior to inferior and from anterior to posterior.
 3. RIB LIFTS
3. RIB LIFTS
Superior Insertion : Transverse process from 7th cervical to 11th thoracic vertebrae
Inferior Insertion : External surface of 1st to 12th rib
Innervation : Corresponding intercostal nerves
Action : Rib Elevation (Inspiratory Action) and Intercostal Stabilization
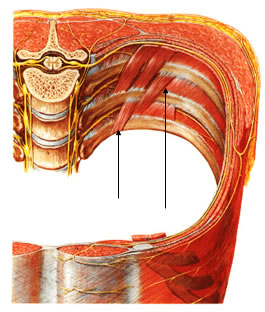
4. SUBCOSTAL
Superior Insertion : Inner surface of overlying rib
Inferior Insertion : Inner surface of the 2nd or 3rd rib below
Innervation : Corresponding intercostal nerves
Action : Intercostal Stabilization
5  . THORAX TRANSVERSE (STERNUM TRIANGULAR)
. THORAX TRANSVERSE (STERNUM TRIANGULAR)
Superior Insertion: Inner face of sternum
Inferior Insertion : Inner surface of 2nd to 6th costal cartilages
Innervation : Corresponding intercostal nerves
Action : Stabilization of the anteroinferior part of the thorax
| CHEST MUSCLES Anterior View - Superficial Dissection |
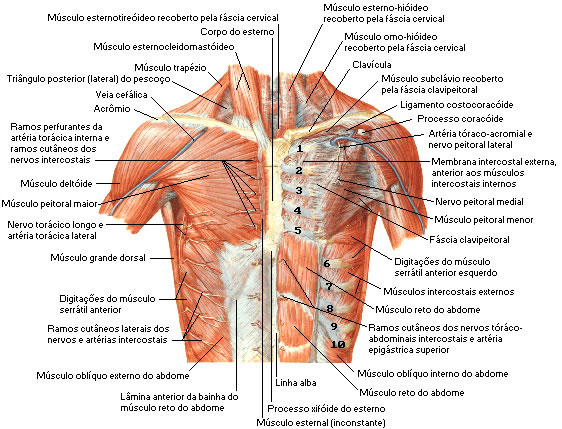 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
| CHEST MUSCLES Anterior View - Deep Dissection |
 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
| CHEST MUSCLES Internal View |
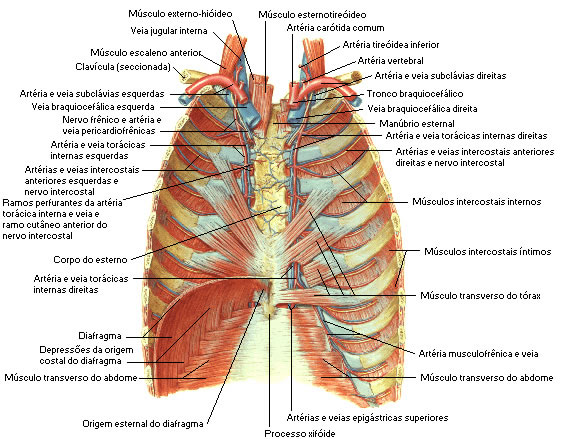 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |