skull as a whole
- Anterior View of the Skull
- Side View of the Skull
- Medial View of the Skull
- Top View of the Skull
- cranial fossae
- Bottom View of the Skull
Anterior View of the Skull
| ANTERIOR VIEW OF THE SKULL |
 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
| ORBIT BONES |
 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
Side View of the Skull
| SIDE VIEW OF THE SKULL |
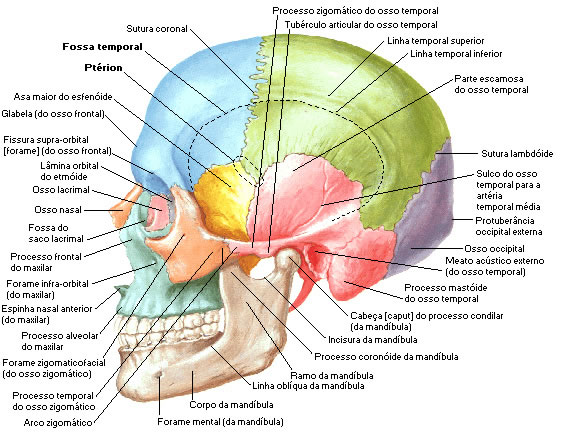 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
| SIDE VIEW OF THE SKULL |
 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
Medial View of the Skull
| MEDIAL VIEW OF THE SKULL |
 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
Superior View of the Skull – Cranial Cap
The top of the skull is called the skull dome or calvaria.
It is crossed by Four Sutures (joints that allow minimal mobility to the bones of the skull):
1 – Coronal or Bregmatic Suture : between the frontal and parietal bones
2 – Sagittal suture : between the two parietals (median sagittal line)
3 – Lambdoid suture : between the parietals and the occiput
4 – Squamous Suture : between the parietal and temporal
Some Anthropometric Points of the Skull :
Bregma – point of union of the sagittal and coronal sutures
Lambda – point of union of the sagittal and lambdoid sutures
Vertex – highest part of the skull
Gonium – angle of the mandible
Pteryum – point of union of parietal, frontal, sphenoid and temporal bones
| TOP VIEW OF THE SKULL - OUTER FACE |
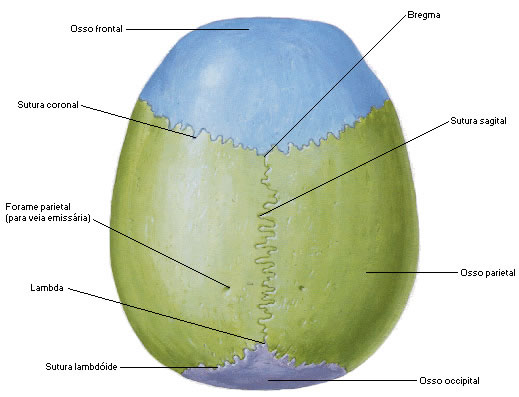 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
cranial fossae
It is divided into 3 pits:
Anterior Fossa Middle Fossa Posterior Fossa

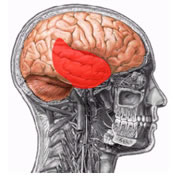
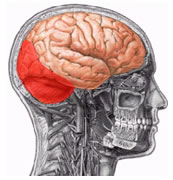
Previous Trench
Limits:
Inner lamina from frontal to posterior edge of lesser wing of sphenoid
Bones:
Frontal, Sphenoid and Ethmoid
Foramina:
- foramen cecum – passage of a small vein from the nasal cavity to the superior sagittal sinus
- Crivous Blade – Passage of the I Cranial Pair (Olfactory Nerve)
- Optical Canal – Passage of the II Cranial Pair (Optic Nerve) and Ophthalmic Artery
Middle Trench
Limits :
Posterior border of lesser wing of sphenoid to superior border of petrous portion of temporalis
Bones :
Sphenoid and Temporal
Foramina :
- Superior Orbital Fissure – Passage of the III Cranial Pair (Oculomotor Nerve), IV Cranial Pair (Trochlear Nerve), V Cranial Pair (Trigeminal Nerve – Ophthalmic Branch), VI Cranial Pair (Abducens Nerve) and the ophthalmic vein
- Round foramen - Passage of the V Cranial Pair (Trigeminal Nerve - Maxillary Branch)
- Foramen Ovale – Passage of the V Cranial Pair (Trigeminal Nerve – Mandibular Branch)
- Spinous foramen - Passage of the middle meningeal artery
- Lacerus or Anterior Torn – nothing passes, is covered by fibrous tissue
- Carotid Canal – Passage of the carotid artery
posterior fossa
Limits:
Superior edge of the temporalis rock to the inner lamina of the occipital bone
Bones:
Temporal and Occipital
Foramina :
- Internal Acoustic Meatus – Passage of VII Cranial Pair (Facial Nerve), VIII Cranial Pair (Vestibulocochlear Nerve)
- Jugular foramen - Passage of the IX Cranial Pair (Glossopharyngeal Nerve), X Cranial Pair (Vagus Nerve) and XI Cranial Pair (Accessory Nerve) and Internal Jugular Vein
- Hypoglossal Canal – Passage of the XII Cranial Pair (Hypoglossal Nerve)
- Condylar Channel – Inconstant
- Foramen Magnus – Passage of the bulb, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, vertebral arteries, spinal roots and accessory nerve
STRUCTURES OF THE CRANIAL FOSS 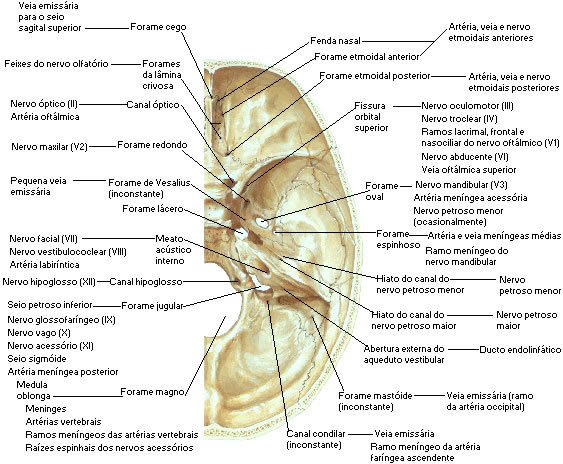
Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. cranial fossa bones 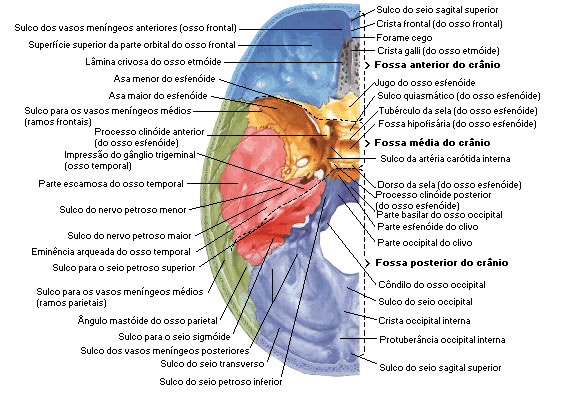
Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000 . Bottom View of the Skull
BOTTOM VIEW OF THE SKULL 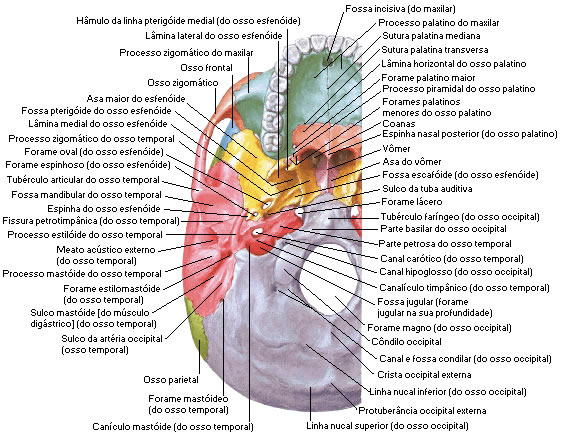
Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000.
