Shoulder blade
It is an even, flat, very thin bone that can be translucent at certain points. It forms the dorsal part of the shoulder girdle.
It has a triangular shape with two faces, three edges and three angles.
faces
Dorsal Face
- Spine of the Scapula – Separates the supraspinatus and infraspinatus fossae
- Acromion – Located at the end of the spine
- Supraspinatus Fossa – It is concave and smooth, located above the spine
- Infraspinous Fossa – It is concave and located below the spine
costal face
subscapularis fossa
edges
Top Edge
- Scapular Notch – Semicircular notch located on the lateral portion and formed by the base of the coracoid process
- Coracoid Process – Thick, curved process near the neck of the scapula
Side Edge
Medial Edge
angles
Bottom Angle – Thick and rough
Top Angle – Thin, smooth and rounded
Side Angle – Is widened in a thick process. Enter the shoulder joint
- Glenoid cavity – It is an excavation of the scapula that articulates with the humerus
- Supraglenoid tubercle – Located above the glenoid cavity
- Infra-Glenoid Tubercle – Located below the glenoid cavity
The Scapula articulates with two bones: Humerus and Clavicle.
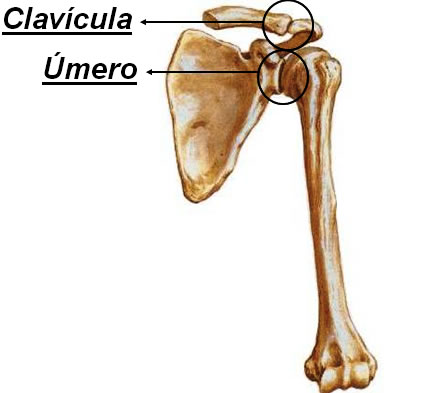 |
| SCAPULA - PREVIOUS VIEW |
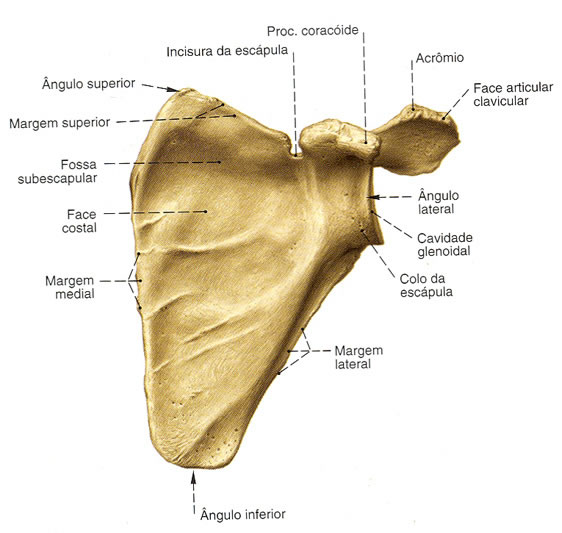 |
| Source: SOBOTTA, Johannes. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 21 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, 2000. |
| SCAPULA - BACK VIEW |
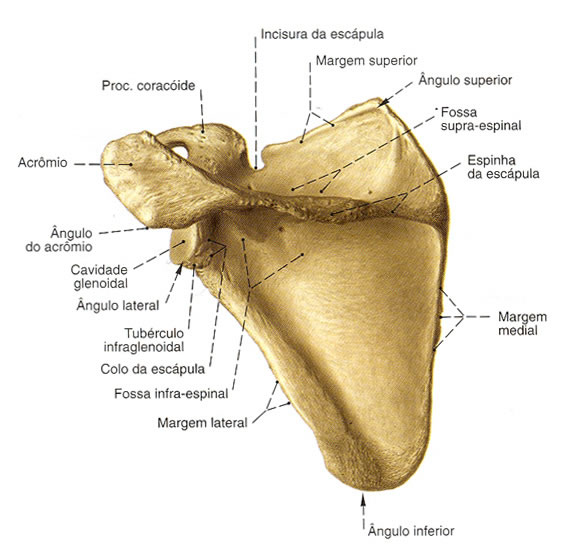 |
| Source: SOBOTTA, Johannes. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 21 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, 2000. |
| SCAPULA - SIDE VIEW |
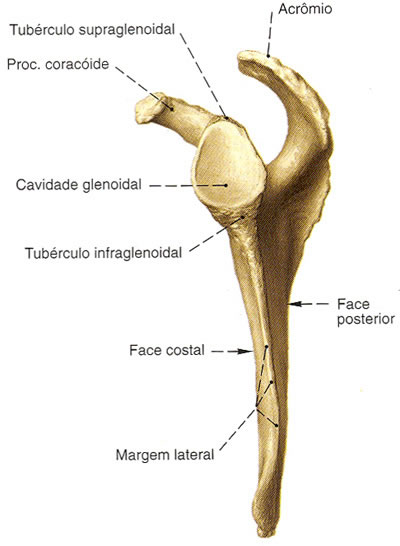 |
| Source: SOBOTTA, Johannes. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 21 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, 2000. |
